Looking Good Info About What Is 1 Phase And 3-phase Electricity

Decoding Electricity
1. Understanding the Basics
Ever wondered what's powering your home appliances versus the massive machines in a factory? The answer often boils down to the type of electrical power they use: single-phase or three-phase. Think of it like this: single-phase is your reliable sedan, while three-phase is a powerful pickup truck. Both get you where you need to go, but they handle different loads. We'll break down the key differences without getting too bogged down in technical jargon.
At its simplest, electrical power is the flow of electrons. In alternating current (AC), which is what we typically use, the direction of this flow reverses periodically. The 'phase' refers to the distribution of this AC power. Knowing the difference between 1 phase and 3-phase electricity is essential for electrical planning and understanding the capabilities of different electrical systems.
Imagine a single-phase system as having one wave of power pushing electrons back and forth. Now, picture a three-phase system as having three waves, offset from each other, pushing those electrons. This difference in the number of 'waves' has significant implications for power delivery and efficiency.
So, why should you even care? Well, if you're planning any significant electrical work, understanding these concepts can save you time, money, and maybe even prevent a few sparks! It also helps you appreciate the complex network that brings electricity to your life, from charging your phone to powering your entire home.

Delving Deeper
2. The Homebody of Power
Single-phase electricity is the standard for residential homes and light commercial applications. It's what powers your lights, refrigerator, TV, and most common household appliances. The beauty of single-phase is its simplicity and cost-effectiveness for lower power demands.
Think of a single-phase circuit as a simple loop. Electricity flows from the power source, through your appliance, and back to the source. It's a straightforward and reliable system for powering everyday necessities. You'll usually see it in systems that require up to around 240 volts. Beyond that, things start getting tricky and less efficient.
While simple, single-phase power does have its limitations. It's not ideal for running large motors or heavy machinery, as it tends to produce vibrations and can be less efficient. Imagine trying to tow a trailer with that sedan we mentioned earlier — it'll get the job done, but it'll struggle a bit.
However, for most homes, single-phase power is more than sufficient. It's the unsung hero that keeps your lights on, your food cold, and your devices charged, without you even having to think about it.
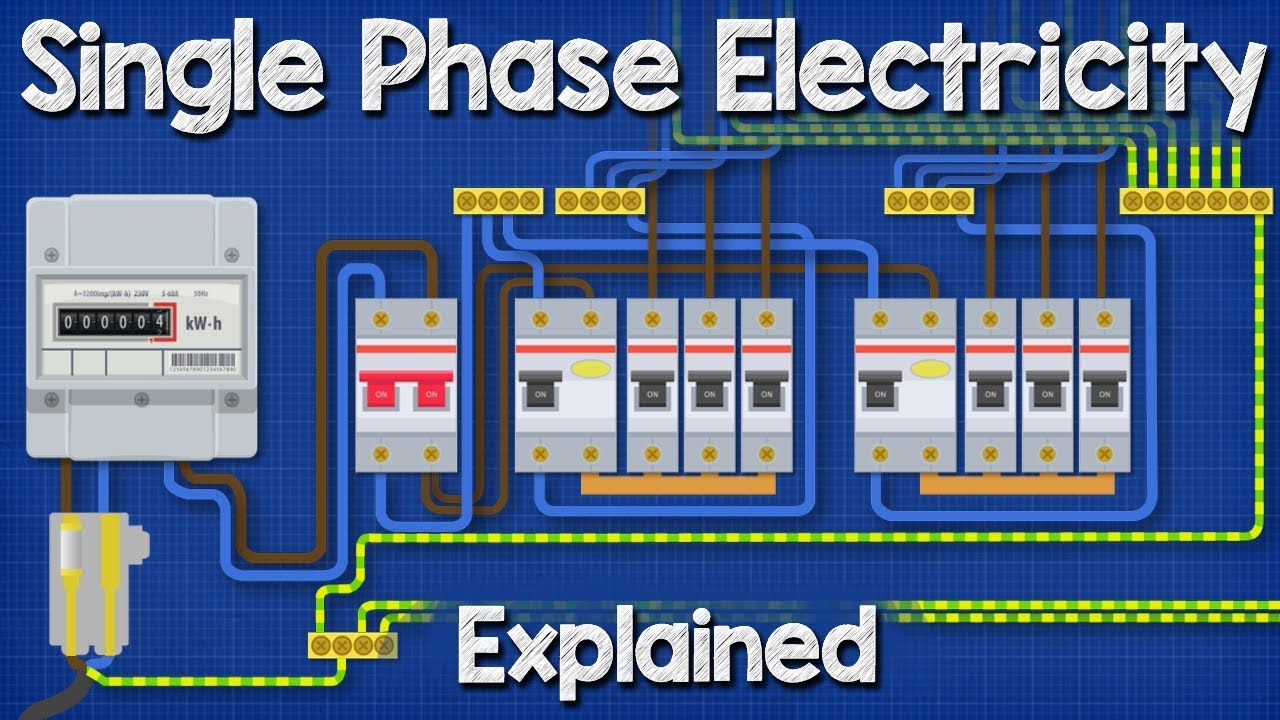
What Is A Single Phase On Diagram Solved Chapter 2
Unleashing the Power
3. The Workhorse of Industry
Three-phase electricity is the powerhouse behind industrial and commercial operations. It's the backbone of factories, hospitals, and large office buildings, providing the muscle needed to run heavy machinery, HVAC systems, and other high-power equipment. This is the power system you want to know when dealing with applications demanding a higher level of energy transmission.
Unlike the single wave of single-phase, three-phase electricity uses three separate waves of power, each offset by 120 degrees. This creates a smoother, more consistent power flow, which is essential for running large motors and other sensitive equipment. This offset ensures that at least one phase is always near its peak voltage, providing a continuous power delivery.
The advantage of three-phase power is its efficiency and ability to handle significantly larger loads compared to single-phase. Those three offset waves mean that equipment runs smoother, quieter, and lasts longer. Imagine that pickup truck easily hauling that same trailer — that's three-phase power in action.
While more complex and costly to install, three-phase electricity is essential for businesses and industries that require substantial power. It's the reliable workhorse that keeps the wheels of commerce turning, literally and figuratively.
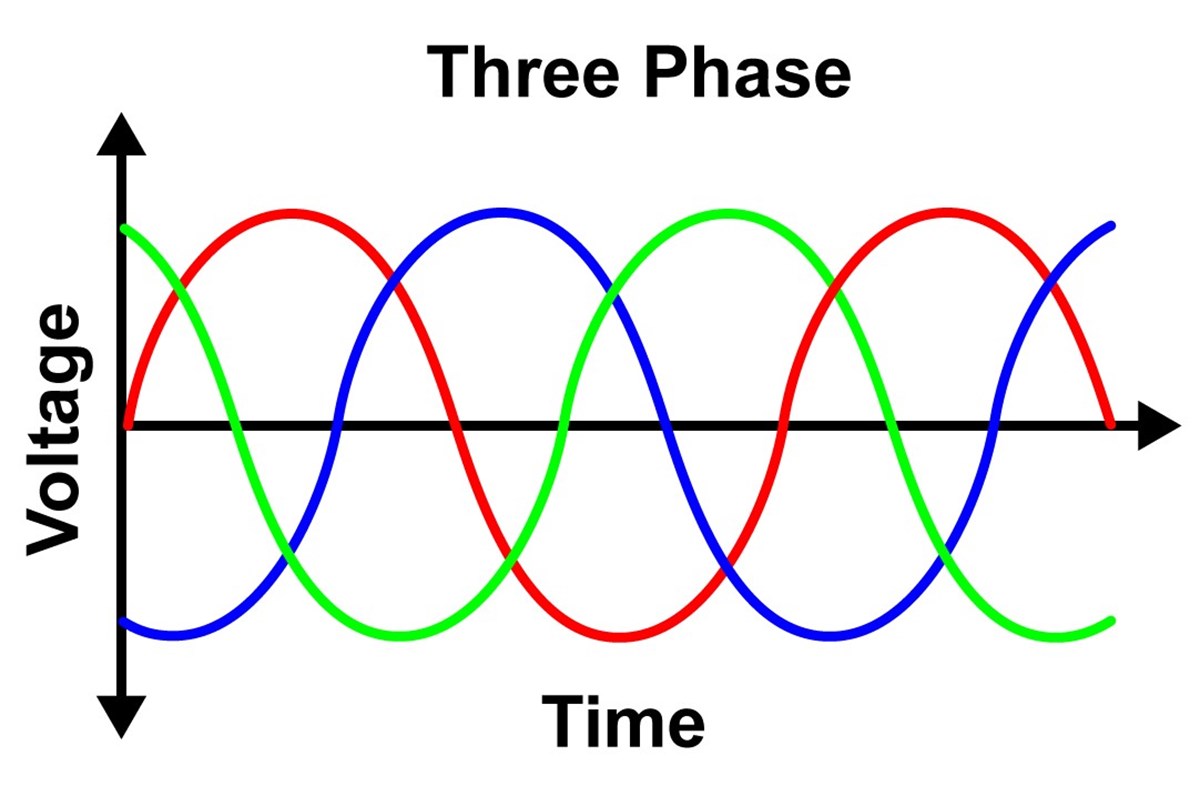
What Is 3 Phase Power? Power Electrics
Choosing the Right Phase
4. Assessing Your Needs
Deciding whether to use single-phase or three-phase electricity depends entirely on your power requirements. For most residential applications, single-phase is the obvious choice. It's simple, affordable, and perfectly adequate for powering your home.
However, if you're running a business that involves heavy machinery, large HVAC systems, or other high-power equipment, three-phase electricity is likely the better option. It's more efficient, more reliable, and can handle significantly larger loads without straining the system. A consultation with a qualified electrician is always recommended before making any decisions.
Consider the long-term implications as well. While three-phase installation may be more expensive initially, the increased efficiency and reliability can save you money in the long run, especially for businesses with high power demands. It's about balancing upfront costs with long-term operational efficiency.
Ultimately, the choice between single-phase and three-phase electricity is about matching the power source to the task at hand. Understanding the differences and considering your specific needs will help you make the right decision for your home or business. Get the right electrical setup to ensure a safe and effective system.

Practical Applications
5. Electricity in Action
To further illustrate the differences, let's look at some real-world examples. Think about your home workshop. A small drill or sander likely runs on single-phase power. But a large table saw or air compressor might require a dedicated 240-volt single-phase circuit, or even three-phase, depending on its size and power demands.
In commercial settings, you'll find single-phase power used for lighting, small appliances, and office equipment. Meanwhile, three-phase powers the elevators, the central air conditioning system, and the manufacturing equipment in the warehouse. Essentially, any high-demand application benefits from three-phase's consistent power delivery.
Hospitals are another prime example of three-phase usage. Medical imaging equipment, life support systems, and large HVAC units all rely on the reliable and consistent power of three-phase electricity. A power fluctuation or outage can have serious consequences in a hospital, so redundancy and stability are paramount.
From the simple convenience of your home to the complex operations of a factory or hospital, single-phase and three-phase electricity play distinct but crucial roles in powering our modern world. By understanding their differences and applications, you can better appreciate the intricate electrical systems that surround us every day.
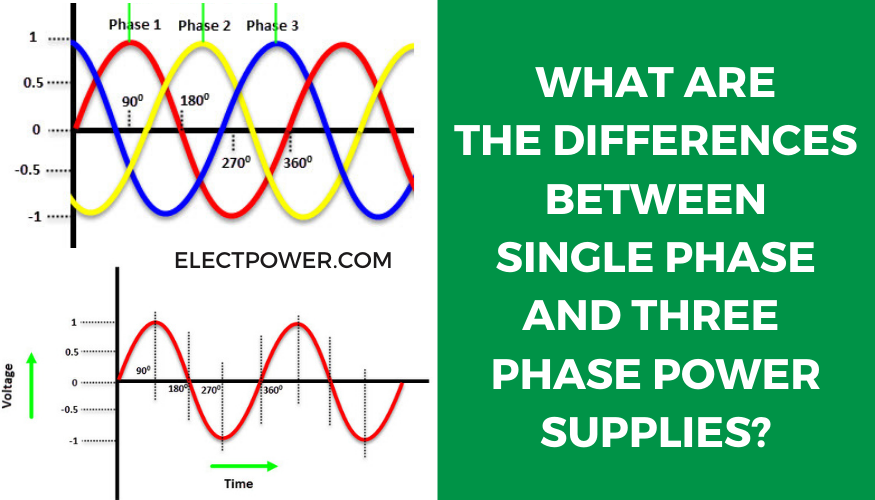
Can A 3 Phase Motor Run On Single Power
FAQ
6. Demystifying Electrical Phases
Q: Can I convert single-phase to three-phase power?
A: Yes, you can! Devices called rotary phase converters or static phase converters can convert single-phase to three-phase power. However, they often come with efficiency losses and are best used for specific applications rather than entire systems. Variable Frequency Drives (VFDs) can also offer a three-phase output from a single-phase input, often while providing motor speed control benefits.
Q: Is three-phase power more dangerous than single-phase?
A: Not necessarily. Both types of power can be dangerous if handled improperly. The higher voltage and current capacity of three-phase systems require extra caution, but with proper safety procedures and qualified electricians, the risk is manageable. Safety is paramount when working with any electrical system.
Q: How can I tell if my business has three-phase power?
A: Look at your electrical panel. Three-phase panels are typically larger and have more breakers than single-phase panels. Also, check your utility bill; it may indicate whether you're being charged for three-phase service. When in doubt, consult a qualified electrician who can properly assess your electrical system.
Q: Is three-phase power more efficient?
A: Generally, yes. For large motors and high-power applications, three-phase power is more efficient because it provides a smoother, more consistent power flow, reducing vibrations and heat, and improving motor lifespan.